2.2 Surface analysis of thermocouple wire
Surface secondary electron morphology of Pt wire
The typical secondary electron morphology image (Second-ary Electron Image, SEI) of the outer surface of pure platinum dual wire is shown in Figure 1a and Figure 1b. It can be seen from Figures 1a and 1b that although the platinum-rhodium 10-platinum wire does not use grain boundary etching technology to show its grains, its grain boundaries are clearly visible, and the grain boundaries are lower than the matrix and sag. This phenomenon shows that The grain boundary of the silk has been damaged during use.
Qualitative and quantitative analysis of the matrix and grain boundary phases in Fig. 1b, the results are shown in Table 1. It can be seen from Table 1 that the P content of the grain boundary phase has reached as high as 3.51% -5.14%. According to the Pt-P phase diagram, the P content in the Pt20P7 phase formed by P and Pt is 5.26%, so the grain boundary phase may be the Pt20P7 phase.
Figure 1c is an enlarged triangular grain boundary morphology. It can be observed that a new phase may have formed in the grain boundary, and cracks exist, showing brittle characteristics. The surface scan analysis showed that P element segregated at the grain boundary. Figure 1d is the distribution diagram of P element on it. It can be seen that P element has obvious segregation.
Analysis and discussion on brittle fracture of platinum-rhodium-platinum-coupling wire of thermocouple in steel factory hot blast stove
Hot blast furnaces in steel mills are very common equipment used by metallurgical enterprises. They use coal, coal gas or natural gas as fuel. The temperature is usually around 1200 ℃. Platinum and rhodium 10-platinum thermocouples are used to measure the temperature. The furnace is a typical reducing atmosphere , Mainly CO2, CO, O2 and N2.
The platinum-rhodium 10-platinum thermocouple has a brittle fracture failure in a reducing atmosphere, usually for the following reasons: ① Hydrogen atoms can penetrate into the platinum metal at high temperature, causing fracture due to hydrogen embrittlement; ② Carbon can dissolve at high temperature In platinum, after cooling, it precipitates out of platinum in a graphite shape, making platinum brittle and easy to break; ③Platinum and platinum-rhodium alloy come into contact with refractory materials containing SiO2 in a reducing atmosphere at high temperature to produce platinum silicide, causing brittle fracture.
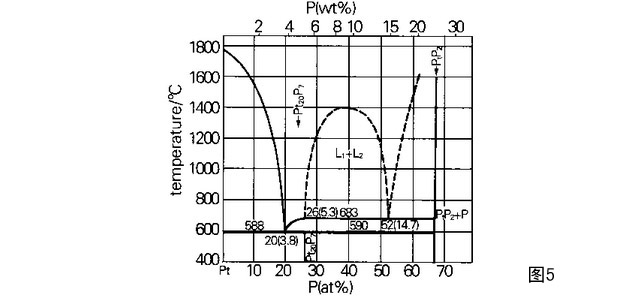
It can be seen from the above test results that the double wire is not caused by the above reasons, but is attacked by P element, and segregation occurs on the grain boundary of the double wire, and the P content of the grain boundary phase has reached 3.51% -5.14 %. According to the Pt-P phase diagram, P and Pt can form a Pt20P7 phase with a P content of 5.26%. Therefore, the P content at the grain boundary of the wire is sufficient to form a Pt20P7 phase. This phase and Pt are easy to form a eutectic, and the eutectic The temperature is only 588 ℃. When using the temperature of 1200 ℃, we can see from the phase diagram of Figure 5 that the metal Pt- coexists with the Pt% of the melt containing P. When the temperature drops, the traces of the melt flow are retained. This can be seen from the figure The grain boundary of 3 shows that the Pt20P7 phase is parallel, and this phase is also relatively brittle, and it is easy to form cracks, as shown in Figure 1c, which eventually causes the even wire to break along the crystal. Therefore, it can be considered that P element is the main cause of broken filaments.
Contact: Tiankang Export Sales Department
Phone: +86-18226665885
Tel: +86-0550-7788337
Email: sales@chinathermocouple.com
Add: No.20# RenHe South Road,TianChang,AnHui Province,China